Flue Gas Treatment Systems
RETOX
Volatile organic compounds (VOC) which are one of the main components used in many industrial process suddenly evaporates when contacted with the air and causes serious health effects and adverse environmental effects.
Although there are several definitions for VOCs, which are one of the main components in many industrial processes, they can simply be defined as organic chemicals that suddenly evaporate when contacted with the air even at room temperatures. In literature, European Union defines VOC as any organic compound having at 293,15 K 20 oC)a vapour pressure of 0,01 kPa or more.
VOCs may result from different activities including thermal processes, use of organic solvent in production processes, transport and handling of liquid fuels and organic compounds such us petrol and its derivatives, refineries and organic chemical industries. In general, all industries using solvents and organic petrochemical products cause VOC emissions.
Inside a processing plant, there are two main locations which can be a VOC emission source. The first one is the process activities itself inside the mixers, storage tanks and so on. Since these are considered as point sources, determination of the VOC emission is relatively easy. A piping system shall be placed into these sources in order to collect the VOCs and send them to the treatment unit. The second source is the fugitive emissions from the process equipment leaks. These fugitive emission sources include emissions during the transportation of the chemicals/solvents within the plant. Therefore, these cannot be point sources and directly increases indoor VOC concentration. Hence, in order for the treatment of those VOCs, a good air ventilation is required inside the plant.
Considering that many industries are using solvent based raw materials or petrochemical compounds in their production, VOC emissions is a common problem for most of the industry sectors. The main industries facing this problem are:
- Paint industry,
- Solvent producers,
- PET and PET film manufacturers,
- Packing industry,
- Printing & lamination,
- Chemical processing,
- Aluminum extrusion painting,
- Can/coil coating,
- Pharmaceutical product manufacturers,,
- Metal finishing & recycling,
- Plastic finishing & recycling,
- Surface cleaning production
Reduce Your Operation Cost with Proper Selection of the Technology!
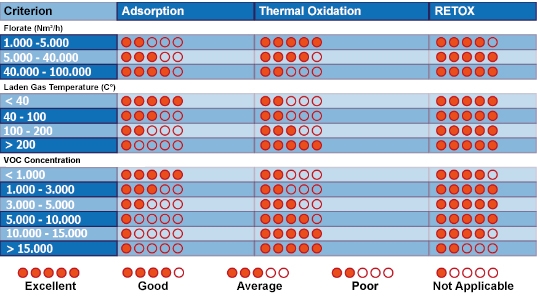
The selection of the technology is a very important step in VOC abatement since the selection of the applicable technology will affect the operation cost of the system.
In adsorption technology, all the process is physical rather than the chemical which results as a limited performance when compared with the other technologies and it is not suitable for all kinds of pollutants. The initial cost of the system is very low; on the other hand the constant requirement of the activated carbon increases the operation costs.
Thermal oxidation systems depend on the chemical oxidation of the compounds and convert the VOC’s to CO2and H2O at very high temperatures (about 850 oC). The destruction efficiency of this technology is very high whereas the fuel consumption is also very high.
Santes provides a cost effective solution with high destruction efficiency having low fuel consumption called RETOX.
VOC Treatment Technologies:
| Adsorption Thermal | Oxidation | RETOX | ||
| Reuse Of Heat In The Treatrent Systems | - | - | + | |
| Heat Recovery Type | - | - | Packed Column | |
| Heat Recovery Efficiency (%) | - | - | 95 | |
|
Chimney Temperature |
30-100oC | 850 oC | 70-150 oC | |
| Maximum Efficiency (%) | 40 | 98-99.99+ | 95-99+ | |
| Operation Cost | High | Very High | Low |

- No fuel consumption when there are enough VOC in the stream,
- Very high removal efficiencies of 99+%,
- Lowest possible operating costs,
- Minimal maintenance requirements,
- Low electricity consumption due to special heat recovery media,
- High thermal recovery efficiency up to 95%,
- Cost effective design and low capital cost,
- Ability to design and manufacture 2 can and 3 can systems,
- Operator friendly solution with PLC integrated system